GaussView¶
GaussView is a graphical interface used with Gaussian. It aids in the creation of Gaussian input files, enables the user to run Gaussian calculations from a graphical interface without the need for using a command line instruction, and helps in the interpretation of Gaussian output (e.g., you can use it to plot properties, animate vibrations, visualize computed spectra, etc.).
Policy¶
Gaussian and GaussView are available to users at HPC2N who are at UMU university. This restriction is due to the licensing agreement with Gaussian.
Citations
You are required to acknowledge Gaussian in scientific papers that have results obtained with it. Please follow the suggestion on the Gaussian citation page.
Overview¶
Gaussian is a program for computing the electronic structure of molecules. Its companion GaussView is a graphical interface that allows you to design molecules and Gaussian input scripts as well as analyze the results from the simulations.
GaussView at HPC2N¶
On HPC2N we have GaussView available as a module on Kebnekaise. To see the available versions, login to Kebnekaise and do ml spider gaussview.
Usage at HPC2N¶
Load GaussView module load gaussview/6.1.1 and start it on the command line vglrun gv. It should look like this:
Then, you can start designing your molecules and input files for Gaussian. Here, there is a small example input.com input file for a water molecule that was supported in old Gaussian versions:
%NProcShared=8
%chk=geom_optim.chk
%mem=16GB
#B3LYP/6-31+G(d) OPT=(ModRedun) SCF=(MaxCycle=256) pop=(mk,dipole) NoSymm
3 atoms structure water, RESP
0 1
O -47.646 -49.315 -52.505
H -47.557 -48.371 -52.637
H -48.284 -49.590 -53.163
In the latest Gaussian version, the number of processors option is now split into the number of cpus and gpus, see Gaussian documentation.
Running a job inside GaussView¶
Besides the standard way to submit jobs to the queue with the sbatch job.sh command on the terminal, one can submit jobs inside GaussView.
In GaussView go to Preferences and in the Job Setup option choose execute using custom command line, and in the box write sbatch job.sh and then Ok:
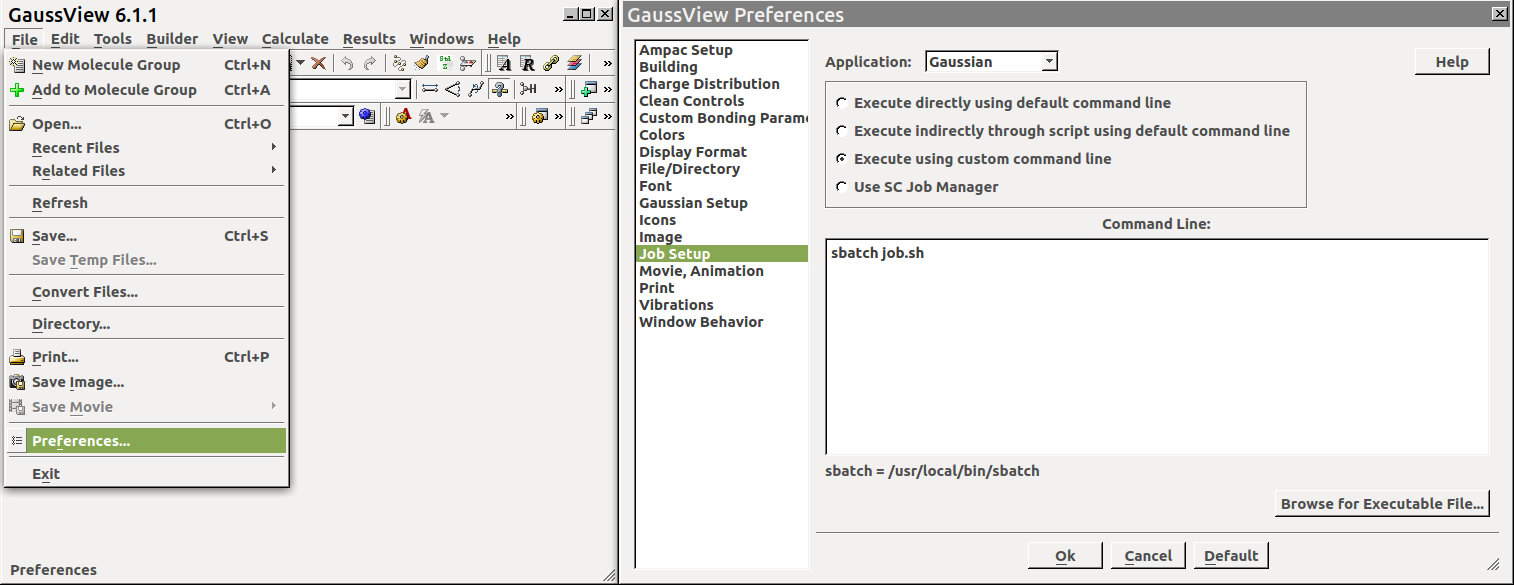
Put this job.sh script in the folder where you opened GaussView fix the project ID, number of cores, and type/number of GPU cards (v100, l40s, …):
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH -A Project_ID
#SBATCH -t 05:10:00 # time
#SBATCH -c X # nr. of cores
#SBATCH --gpus-per-node=Type:1 # type of GPUs
#SBATCH --output=job_str.out
#SBATCH --error=job_str.err
ml purge > /dev/null 2>&1
ml gaussian/16.C.02-AVX2
nvidia-smi
# For Gaussian 16 set the %Cpu parameter (and %GpuCpu if GPUs have been requested)
g16.set-cpu+gpu-list input.com
# Start Gaussian, example here is assuming Gaussian 16
g16 input.com
g16.set-cpu+gpu-list will set the list of CPUs and GPUs automatically even if the script is from an older version of Gaussian.
Then, go to Gaussian Calculation Setup and Submit the job:
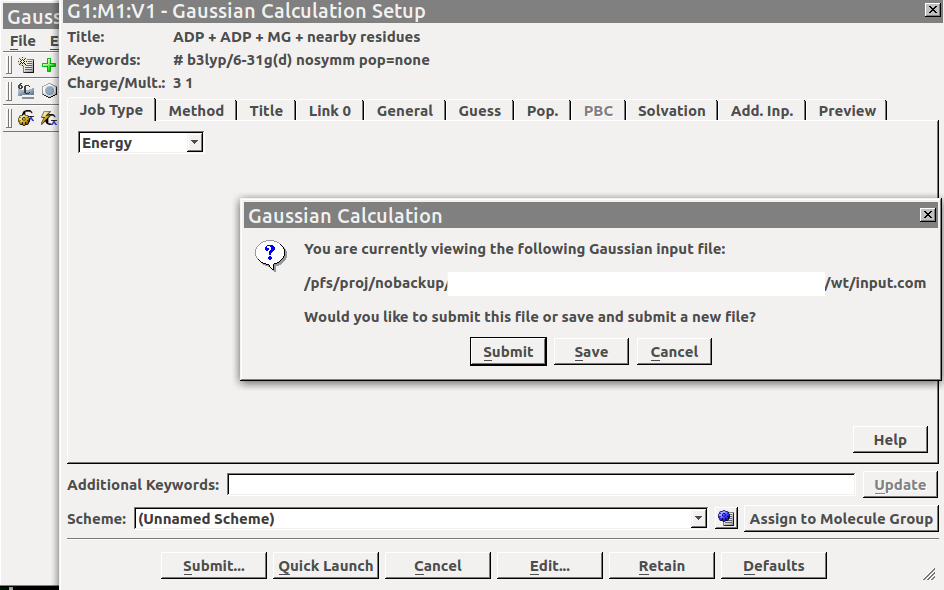
A warning message on the termination of the job without producing a log file will appear and you can OK to close this window.
You can check that the job is in the queue with the squeue --me command on the terminal.
Additional info¶
Additional information can be obtained from the Gaussian & GaussView tutorial videos.